
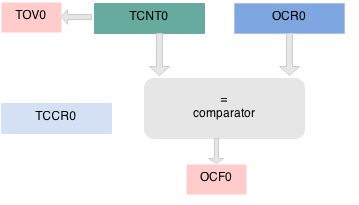
You can also invert the output PWM by changing the values of bits (COM00 and COM01) in the TCCR register. The below timing diagram explains the operation. When the value of TCNT0 matches the OCR0, it’s called a Compare Match.
#Codevision timer examples software
This compare value is set by the software in a register called OCR0 (Output Compare Register), while the value of the counter itself is contained in a register called TCNT0. The Output pin (OC0) is cleared when the counter reaches a certain value called the “ Compare value” while up counting, and is set when the counter reaches the same value while down counting. In “ Phase Correct PWM” mode, the counter counts repeatedly from 0 to its maximum value (0xFF) and then back from the maximum to zero. Atmega32 has 3 timer/counters and we are using timer/counter 0.
#Codevision timer examples how to
This module can be used in several modes to generate different PWM signals of different characteristics here we shall explain how to use the counter in the “Phase Correct PWM” mode.
In order to get the PWM from AVR, we need to use the timer/counter module of the AVR. In this article, we will explain how to get a PWM from the AVR Atmega32 and we shalll apply the output PWM to a small DC motor to vary its speed. Using PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) to control a device is a common practice in embedded systems for example, you can use it to control the light intensity of a LED or control the speed of a DC motor. How to control DC motor speed using PWM on Atmega32


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
